Antiplatelet Drugs: What They Are, How They Work, and What You Need to Know
When your blood starts to clot too much, it can block arteries and trigger a heart attack or stroke. That’s where antiplatelet drugs, medications that stop platelets from clumping together to form dangerous clots. Also known as blood thinners, they don’t actually thin your blood—they stop the cells that trigger clotting from sticking together. Unlike anticoagulants that work on clotting factors, antiplatelet drugs target your platelets directly. This makes them essential for people with heart disease, those who’ve had stents placed, or anyone who’s had a previous clot-related event.
Two of the most common aspirin, a simple, low-cost drug that’s been used for decades to block platelet activation, and clopidogrel, a stronger option often paired with aspirin after a stent or heart attack. Others include prasugrel and ticagrelor—each with different strengths, side effects, and timing needs. These aren’t just pills you take once; they’re long-term tools that require careful management. Skipping doses or stopping without talking to your doctor can be dangerous. And while they reduce clot risk, they also raise bleeding risk, so you need to know the signs: unusual bruising, nosebleeds, dark stools, or prolonged bleeding from cuts.
Many of the posts in this collection focus on how these drugs interact with other treatments. You’ll find comparisons between antiplatelet drugs and other cardiovascular medications, like warfarin or newer anticoagulants. You’ll also see how diet, supplements, and even over-the-counter painkillers can interfere with their action. For example, some herbal supplements can thin your blood further, while others may block the drug’s effect entirely. If you’re on one of these drugs, knowing what to avoid is just as important as knowing how to take it.
There’s no one-size-fits-all antiplatelet plan. Your age, medical history, and other conditions—like diabetes, kidney disease, or a history of ulcers—all shape which drug and dose is right for you. Some people need just aspirin. Others need dual therapy for months or even years. And for some, the risks outweigh the benefits. The articles here give you real-world guidance: how to spot side effects, what to do if you miss a dose, how to talk to your doctor about switching, and when to get tested for drug resistance. This isn’t theoretical. These are the questions real patients ask every day.
Compare Aggrenox (Dipyridamole) with Alternatives for Stroke Prevention
Compare Aggrenox (dipyridamole/aspirin) with alternatives like aspirin alone, clopidogrel, and dual therapy for stroke prevention. Learn which works best, side effects, cost, and what to do if you can't tolerate it.
About
Medications
Latest Posts


How to Spot a Pharmacy Labeling Error Before Taking a Medication
By Marcel Kornblum Dec 21, 2025
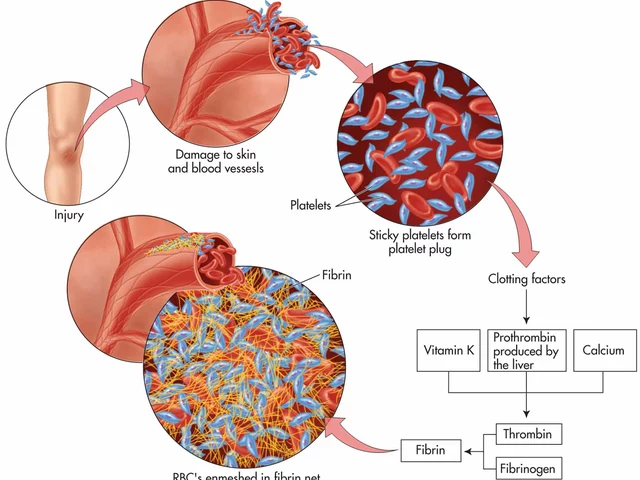
The psychological impact of blood clots in stents: coping strategies and support
By Marcel Kornblum Jul 1, 2023

How to Buy Cheap Generic Metformin Online - A Safe, Fast Guide
By Marcel Kornblum Sep 24, 2025